
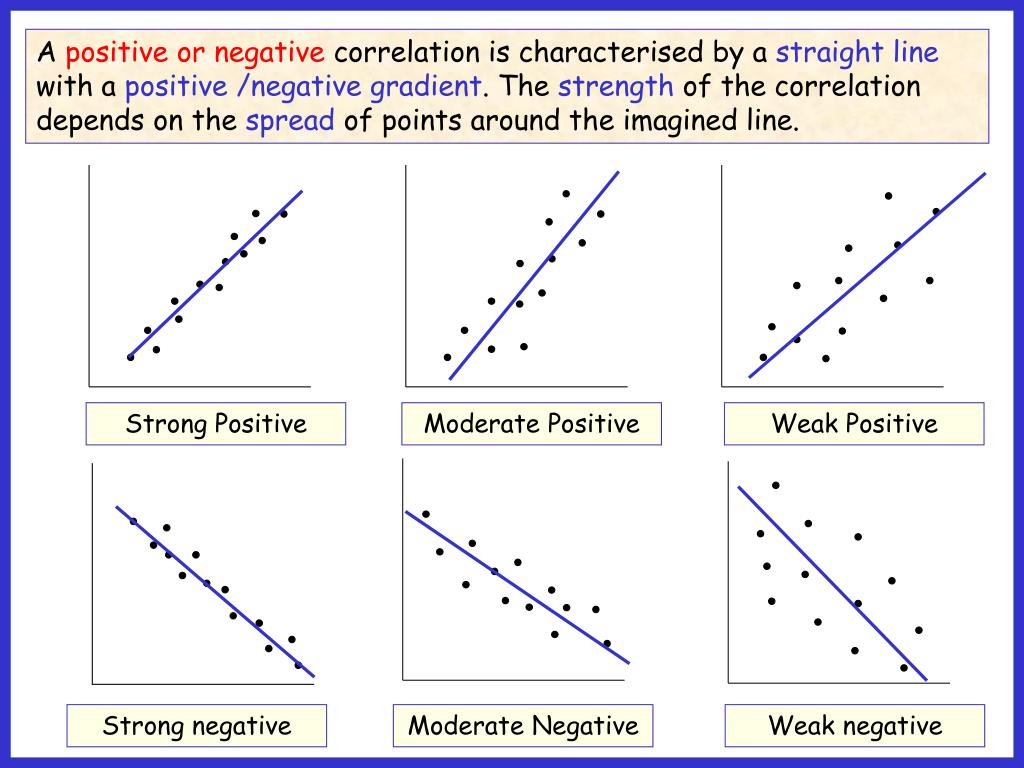
For example, if most studies in your field have correlation coefficients nearing. While this guideline is helpful in a pinch, it’s much more important to take your research context and purpose into account when forming conclusions. You can use the table below as a general guideline for interpreting correlation strength from the value of the correlation coefficient. There are many different guidelines for interpreting the correlation coefficient because findings can vary a lot between study fields. The absolute value of a correlation coefficient tells you the magnitude of the correlation: the greater the absolute value, the stronger the correlation. The absolute value of a number is equal to the number without its sign. The sign of the coefficient reflects whether the variables change in the same or opposite directions: a positive value means the variables change together in the same direction, while a negative value means they change together in opposite directions.

The value of the correlation coefficient always ranges between 1 and -1, and you treat it as a general indicator of the strength of the relationship between variables. 58.ĭiscover proofreading & editing Interpreting a correlation coefficient The correlation coefficient is strong at. Correlation analysis exampleYou check whether the data meet all of the assumptions for the Pearson’s r correlation test.īoth variables are quantitative and normally distributed with no outliers, so you calculate a Pearson’s r correlation coefficient. You calculate a correlation coefficient to summarize the relationship between variables without drawing any conclusions about causation. Then you can perform a correlation analysis to find the correlation coefficient for your data. After removing any outliers, select a correlation coefficient that’s appropriate based on the general shape of the scatter plot pattern. There are many different correlation coefficients that you can calculate. You visualize the data in a scatterplot to check for a linear pattern: Visual inspection exampleYou gather a sample of 5,000 college graduates and survey them on their high school SAT scores and college GPAs. A linear pattern means you can fit a straight line of best fit between the data points, while a non-linear or curvilinear pattern can take all sorts of different shapes, such as a U-shape or a line with a curve. Visually inspect your plot for a pattern and decide whether there is a linear or non-linear pattern between variables. It doesn’t matter which variable you place on either axis. You predict that there’s a positive correlation: higher SAT scores are associated with higher college GPAs while lower SAT scores are associated with lower college GPAs.Īfter data collection, you can visualize your data with a scatterplot by plotting one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Correlational research exampleYou investigate whether standardized scores from high school are related to academic grades in college. In correlational research, you investigate whether changes in one variable are associated with changes in other variables. Comparing studiesĪ correlation coefficient is also an effect size measure, which tells you the practical significance of a result.Ĭorrelation coefficients are unit-free, which makes it possible to directly compare coefficients between studies. You can use an F test or a t test to calculate a test statistic that tells you the statistical significance of your finding. If your correlation coefficient is based on sample data, you’ll need an inferential statistic if you want to generalize your results to the population. A correlation coefficient is a bivariate statistic when it summarizes the relationship between two variables, and it’s a multivariate statistic when you have more than two variables. That means that it summarizes sample data without letting you infer anything about the population. Summarizing dataĪ correlation coefficient is a descriptive statistic. What does a correlation coefficient tell you?Ĭorrelation coefficients summarize data and help you compare results between studies. Frequently asked questions about correlation coefficients.What does a correlation coefficient tell you?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
